About Me
|
|
A natural tinkerer and visual thinker, I have a passion for figuring out how things work and the creation of interesting prototypes. While completing my M.Sc thesis in Human-Computer Interaction on a novel method for calibration-free eye tracking, I was involved with the development of several gaze-aware, cross-disciplinary projects such as attentive privacy glass, gaze-aware artistic paintings, and a media installation that used a user's movements to generate real-time interactive visualizations synchronized to music. In my spare time I am into running, photography, playing volleyball, and actively seeking out new foods and interesting places to consume (delicious) empty calories. |
Technical Experience
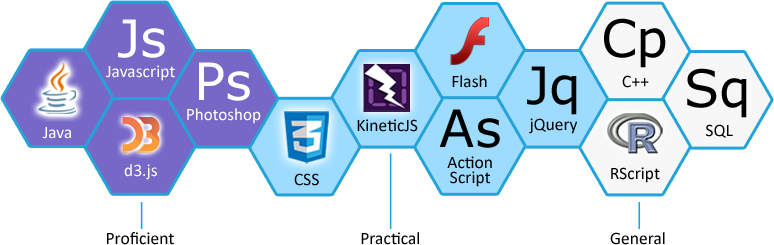
Selected Projects
Oculus Info Inc
Senior developer on ApertureJS, a Javascript-based framework for rapid prototyping and deployment of data visualizations and web-based applications. Duties included development of prototypes, system architecture, and demonstrative web applications. Experience with visualization design and general knowledge of web-based standards.
Oculus Info Inc
Team lead for development of system architecture, UI workflows, and application implementation. Designed and implemented initial prototype for client evaluation, as well as graphic design of iconography used throughout application. The project concluded with an on-site training and user evaluation cycle that included rapid deployment of bug fixes and feature implementation over a 5-day site visit.
Oculus Info Inc
Rapid development of a Flex-based UI and integration with several Java services for a Fortune 500 company - a leader in business analytics, financial visualizations, equity trading and data services. This 4 month project required rapid familiarization with the client's code base and MVC framework. Details and prior knowledge of the project were not provided until arriving on-site at the client's corporate headquarters. Short and seamless integration with an existing agile team was crucial to the successful conclusion of this project.
Computational Linguistics Group, University of Toronto
Designed UI and implemented a Flash/AS3 application for evaluating the efficacy of various techniques for assembling user summaries from previously recorded lecture videos with transcribed audio. Application was deployed to a desktop evaluation environment via Adobe Air.
Elixir Nightclub, Kingston
Designed a software architecture that applied techniques from computer vision and graphics to manipulate and blend live camera feeds with video content for composing visualizations as a real-time performance art, synchronized to music from a live DJ.
Electrical and Computer Engineering, Queen's University
Developed and improved computer vision algorithms for real-time image analysis and object recognition, and dynamic multi-obstacle avoidance. Achieved 3rd place in local Professional Engineers of Ontario (PEO) Thesis Competition (2002). Competed in First American RoboCup at Carnegie Melon University (2003) as a member of Team gEEk.
Patents
Method and Apparatus for Calibration-Free Eye Tracking Using Multiple Glints or Surface Reflections
U.S. Patent No. 7963652
Publications
Tile Based Visual Analytics for Twitter Big Data Exploratory Analysis
In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Big Data 2013
Santa Clara, CA, 2013 (In Press)
Interactive Data Exploration with "Big Data Tukey Plots"
In Proceedings of IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 2013
Atlanta, GA, 2013 (In Press)
AuraOrb: Social Notification Appliance
In Extended Abstracts of ACM CHI 2006 Conference on Human-Factors in Computing Systems
Quebec, Canada, 2006
Media EyePliances: Using Eye Tracking for Remote Control Focus Selection of Appliances
In Extended Abstracts of ACM CHI 2005 Conference on Human-Factors in Computing Systems
Portland, OR, 2005
OverHear: Augmenting Attention in Remote Social Gatherings Through Computer-Mediated Hearing
In Extended Abstracts of ACM CHI 2005 Conference on Human-Factors in Computing Systems
Portland, OR, 2005
Attentive Headphones: Augmenting Conversational Attention with a Real World TiVo
In Extended Abstracts of ACM CHI 2005 Conference on Human-Factors in Computing Systems
Portland, OR, 2005
AttentiveDisplay: Paintings as Attentive User Interfaces
In Extended Abstracts of ACM CHI 2004 Conference on Human-Factors in Computing Systems
Vienna, Austria, 2004
Augmenting and Sharing Memory with eyeBlog
In Proceedings of 1st ACM Workshop on Continuous Archival and Retrieval of Personal Experiences
New York City, NY, 2004
Eye Contact Sensing Glasses for Attention-Sensitive Wearable Video Blogging
In Extended Abstracts of ACM CHI 2004 Conference on Human-Factors in Computing Systems
Vienna, Austria, 2004
ECSGlasses and EyePliances: Using Attention to Open Sociable Windows of Interaction
In Proceedings of ACM Eye Tracking Research and Applications Symposium 2004
San Antonio, TX, 2004
An Eye for an Eye: A Performance Evaluation Comparison of the LC Technologies and Tobii Eye Trackers
In Proceedings of ACM Eye Tracking Research and Applications Symposium 2004
San Antonio, TX, 2004
Queen's University: Soccer Robots
This project involved the development and refinement of computer vision algorithms for real-time image
analysis and object recognition, as well as dynamic multi-obstacle avoidance.
Our team achieved 3rd place in the local Professional Engineers of Ontario (PEO) Thesis
Competition (2002) and subsequently competed in the First American RoboCup at Carnegie
Melon University (2003).
Sample footage of the computer vision navigation and obstacle avoidance systems
Application for Evaluation of User-authored Summaries
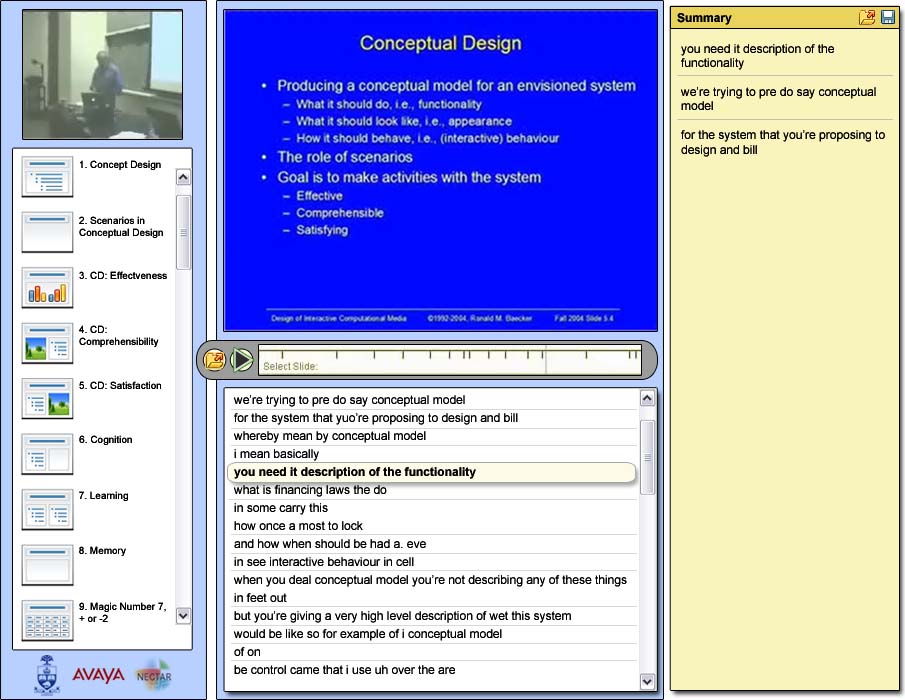
A draft of the user interface design
Left:
The image at the top-left was a running video of the web lecture. Below that was a table of contents (TOC) listing all the slides of that lecture. Clicking on a slide in the TOC would advance the video and the transcription to the appropriate time index.
Centre:
The current slide being discussed was shown at the top of the centre panel. The bar in the middle of the panel contained the video navigation controls. The user could skip to a specific time index in the video by clicking on the timeline to the right of the play button. The minor tick marks in the timeline represented the start of a new slide, while the major tick mark indicated the current time index. The bottom portion of the panel displayed the running transcription of the lecture.
Right:
This panel was for creating user summaries of the lecture. Various techniques for populating this panel were evaluated as part of this study.
Website: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/compling/
Elixir Nightclub: Performance Artist
Designed a software architecture that applied techniques from computer vision and graphics to manipulate and blend live camera feeds with video content for composing visualizations as a real-time performance art, synchronized to music from a live DJ.
Demo footage from an early system prototype
M.Sc Computer Science: Human Media Lab (HML)
Completed M.Sc thesis in Human-Computer Interaction on a novel method for calibration-free eye tracking using computer vision.
From the HML Blog:
"The Human Media Lab is one of Canada's premier media laboratories. Its mandate is to develop disruptive technologies and new ways of working with computers that are viable 10 to 20 years from now. We are currently working on the design of organic user interfaces (oui!), an exciting new paradigm that allows computers to have any shape or form."
(04/2013)
The Discovery Channels features the Human Media Lab on an episode of The Daily Planet
Method and Apparatus for Calibration-Free Eye Tracking Using Multiple Glints or Surface Reflections
ABSTRACT
A method and apparatus for eye gaze tracking in human or animal subjects without calibration of cameras, specific measurements of eye geometries, or tracking of a cursor image on a screen by the subject through a known trajectory. One embodiment provides a method for tracking a user's eye gaze at a surface, object, or visual scene, comprising:
- an imaging device for acquiring images of at least one of the user's eyes
- modeling, measuring, estimating, and/or calibrating for the user's head position
- providing one or more markers associated with the surface, object, or visual scene for producing corresponding glints or reflections in the user's eyes
- analyzing the images to find said glints or reflections and/or the pupil
- determining eye gaze of the user upon a said one or more markers as indicative of the user's eye gaze at the surface, object, or visual scene
Tile Based Visual Analytics for Twitter Big Data Exploratory Analysis (In Press)
ABSTRACT
New tools for raw data exploration and characterization of “big data” sets are required to suggest initial hypotheses for testing.
The widespread use and adoption of web-based geo maps have provided a familiar set of interactions for exploring extremely large geo data spaces
and can be applied to similarly large abstract data spaces. Building on these techniques, a tile based visual analytics system (TBVA) was
developed that demonstrates interactive visualization for a one billion point Twitter dataset. TBVA enables John Tukey-inspired exploratory data
analysis to be performed on massive data sets of effectively unlimited size.
Interactive Data Exploration with "Big Data Tukey Plots" (In Press)
ABSTRACT
Before testing hypotheses, confirmatory data analysis benefits from first examining the data to suggest hypotheses to be tested. This is known as
exploratory data analysis (EDA). Our goal is to develop new automated tools to produce effective raw data characterization on extremely large datasets.
This paper reports on the development of a web based interactive scatter plot prototype that uses tile-based rendering similar to geographic maps and
interaction paradigms. Geographic maps share much in common with scatter plots. Both feature continuous data along two dimensions, use of layering and
legends, axes and scales. Web delivery of maps using tiled rendering has benefitted from years of work. With widespread use, map interactions have become
familiar and make exploration of an abstract large data space easy, even enjoyable. Using similar techniques, our big data tile rendering for scatter
plots provides interactive data exploration with continuous zooming on hundreds of millions of points.
AuraOrb: Social Notification Appliance
ABSTRACT
One of the problems with notification appliances is that they can be distracting when providing information not of immediate interest to the user. In this paper, we present AuraOrb, an ambient notification appliance that
deploys progressive turn taking techniques to minimize notification disruptions. AuraOrb uses eye contact
sensing to detect user interest in an initially ambient light notification. Once detected, it displays a text
message with a notification heading visible from 360 degrees. Touching the orb causes the associated
message to be displayed on the user's computer screen.
Media EyePliances: Using Eye Tracking for Remote Control Focus Selection of Appliances
ABSTRACT
This paper discusses the use of eye contact sensing for focus selection operations in remote controlled media appliances. Focus selection with remote controls tends to be cumbersome as selection buttons place the remote in a device-specific modality. We addressed this issue with the design of Media EyePliances, home theatre appliances augmented with a digital eye contact sensor. An appliance is selected as the focus of remote commands by looking at its sensor. A central server subsequently routes all commands provided by remote, keyboard or voice input to the focus EyePliance. We discuss a calibration-free digital eye contact sensing technique that allows Media EyePliances to determine the user's point of gaze.
OverHear: Augmenting Attention in Remote Social Gatherings Through Computer-Mediated Hearing
ABSTRACT
One of the problems with mediated communication systems is that they limit the user's ability to listen to informal conversations of others within a remote space. In what is
known as the Cocktail Party phenomenon, participants in noisy face-to-face conversations are able to focus their
attention on a single individual, typically the person they look at. Media spaces do not support the cues necessary to
establish this attentive mechanism. We addressed this issue in our design of OverHear, a media space that augments the
user's attention in remote social gatherings through computer mediated hearing. OverHear uses an eye tracker
embedded in the webcam display to direct the focal point of a robotic shotgun microphone mounted in the remote space.
This directional microphone is automatically pointed towards the currently observed individual, allowing the user to OverHear this person's conversations.
Attentive Headphones: Augmenting Conversational Attention with a Real World TiVo
ABSTRACT
Computer users in public transportation, coffee shop or cubicle farm environments require sociable ways to filter out noise generated by other people. Current use of noise-canceling headsets is detrimental to social interaction
because these headsets do not provide context-sensitive filtering techniques. Headsets also provide little in terms of services that allow users to augment their attentive capabilities, for example, by allowing them to pause or fast-forward conversations. We addressed such issues in our design of Attentive Headphones, a noise-cancelling headset sensitive to nonverbal conversational cues such as eye gaze.
The headset uses eye contact sensors to detect when other people are looking at the wearer. Upon detecting eye gaze, the headset automatically turns off noise-cancellation, allowing users to attend to a request for attention. The
headset also supports the execution of tasks that are parallel to conversational activity, by allowing buffering and fast-forwarding of conversational speech. This feature also allows users to listen to multiple conversations at once.
AttentiveDisplay: Paintings as Attentive User Interfaces
ABSTRACT
In this paper we present ECS Display, a large plasma screen that tracks the user's point of gaze from a distance, without
any calibration. We discuss how we applied ECS Display in the design of Attentive Art. Artworks displayed on the ECS
Display respond directly to user interest by visually highlighting areas of the artwork that receive attention, and
by darkening areas that receive little interest. This results in an increasingly abstract artwork that provides guidance to
subsequent viewers. We believe such attentive information visualization may be applied more generally to large screen
display interactions. The filtering of information on the basis of user interest allows cognitive load associated with large display visualizations to be managed dynamically
Augmenting and Sharing Memory with eyeBlog
ABSTRACT
eyeBlog is an automatic personal video recording and publishing system. It consists of ECSGlasses [1], which are a pair of glasses augmented with a wireless eye contact and
glyph sensing camera, and a web application that visualizes the video from the ECSGlasses camera as chronologically
delineated blog entries. The blog format allows for easy annotation, grading, cataloging and searching of video
segments by the wearer or anyone else with internet access. eyeBlog reduces the editing effort of video bloggers by
recording video only when something of interest is registered by the camera. Interest is determined by a
combination of independent methods. For example, recording can automatically be triggered upon detection of
eye contact towards the wearer of the glasses, allowing all face-to-face interactions to be recorded. Recording can also
be triggered by the detection of image patterns such as glyphs in the frame of the camera. This allows the wearer to
record their interactions with any object that has an associated unique marker. Finally, by pressing a button the user can manually initiate recording.
Eye Contact Sensing Glasses for Attention-Sensitive Wearable Video Blogging
ABSTRACT
We present ECSGlasses: eye contact sensing glasses that report when people look at their wearer. When eye contact
is detected, the glasses stream this information to appliances to inform these about the wearer's engagement.
We present one example of such an appliance, eyeBlog, a conversational video blogging system. The system uses eye
contact information to decide when to record video from the glasses' camera.
ECSGlasses and EyePliances: Using Attention to Open Sociable Windows of Interaction
ABSTRACT
We present ECSGlasses: wearable eye contact sensing glasses that detect human eye contact. ECSGlasses report eye contact to
digital devices, appliances and EyePliances in the user's attention space. Devices use this attentional cue to engage in a more
sociable process of turn taking with users. This has the potential to reduce inappropriate intrusions, and limit their disruptiveness.
We describe new prototype systems, including the Attentive Messaging Service (AMS), the Attentive Hit Counter, the first
person attentive camcorder eyeBlog, and an updated Attentive Cell Phone. We also discuss the potential of these devices to
open new windows of interaction using attention as a communication modality. Further, we present a novel signal-encoding
scheme to uniquely identify EyePliances and users wearing ECSGlasses in multiparty scenarios.
An Eye for an Eye: A Performance Evaluation Comparison of the LC Technologies and Tobii Eye Trackers
ABSTRACT
Eye-tracking systems have been employed in many diverse fields, including psychology, cognitive science, disability rehabilitation
research, and human-computer-interaction (HCI). Although numerous studies have been conducted involving applications of eye tracking,
few studies have compared the actual eye-tracking systems themselves. We empirically evaluated the system characteristics of two
independent eye-tracking products using the following parameters: accuracy, reliability, robustness, ease of setup, ease of development,
API capabilities, and real-time performance as metrics. As well, we qualitatively evaluated the various analytical software tools and
features provided by each eye-tracker.
